
You have many options when choosing a vehicle for your investment dollars and it's important to understand the average investment return so you can plan efficiently for your financial future.
Each type of investment option (often called an asset class) comes with its own risks and rewards. If you're investing in the short-term, you need to be more careful about understanding the risks of particular investments. But if you have a long-term investment horizon, the ups and downs tend to even out over time.
Thanks to the power of compound interest, the younger that you start, the less you have to worry about the stock market crashing. If you're starting to invest when you're young, the most important thing to remember is to keep putting money in, even if (especially if) the market goes through a downturn.
When you're in your 20s and 30s, with potentially 30 or 40 years or more to retirement, you can afford to take on more risk with your investments, since you won't need the money for a long time.
The Average Investment Return By Asset Class
Using data from The Measure of a Plan and SSA.gov, we measured the average annual return of a variety of different types of assets. The numbers in the chart below represent the CAGR (Compound annual growth rate) for several different asset classes.
The data is from 1985 to 2020.
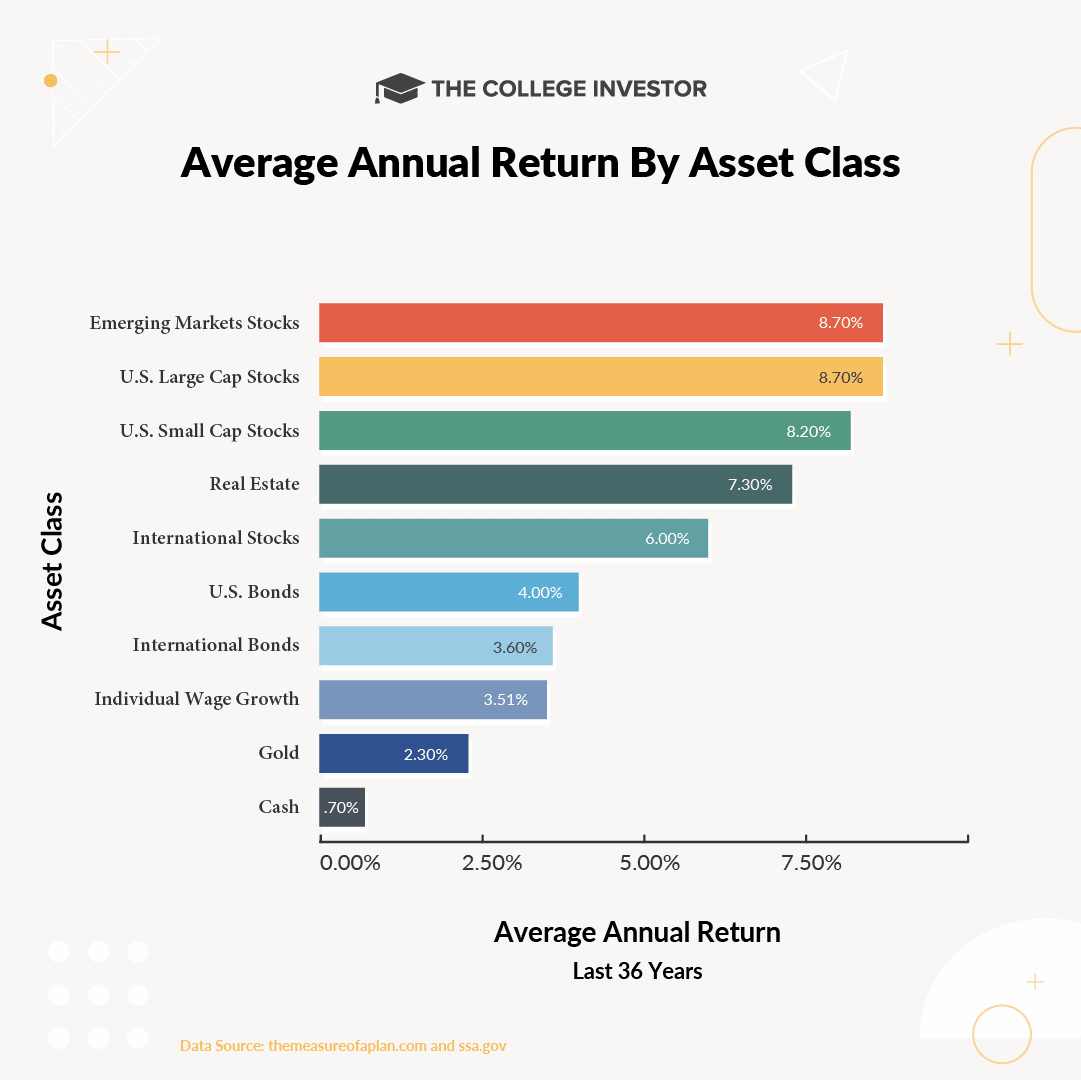
As you can see, stocks have the highest average investment return over this time period, though there is some difference depending on the exact type of stocks you're investing in. Real estate also comes with a sizable average annual return. Next are bonds, then wage growth, gold, and finally cash.
Proper asset allocation is crucial, and the ideal asset allocation will change over time as you get older and closer to retirement. If you're looking at where to put your investment dollars, you may want additional information on each of these asset classes.
For each asset class, we have also included the Vanguard index fund that invests in this asset class (read our Vanguard review).
Stocks: Large Cap, Small Cap, International, Emerging Markets
Stocks are an asset class that tends to have the highest return of any type of investment, but they also tend to have higher-than-average volatility. This isn't necessarily a problem if you have a long time horizon, but if you are older, retiring soon, or have a more immediate need for your money, you might not want to be heavily invested in stocks.
But it's important to remember that "stocks" isn't a one-size-fits-all asset class. There are a variety of "types" of stocks, since stocks just represent ownership in a company.
Large Cap: Large cap stocks are companies with a market cap over $10 billion. These are basically the biggest companies in the United States.
Small Cap: Small cap stocks are companies with a market cap under $2 billion. These are the smaller "up and coming" companies in the United States.
International: These are companies that are non-US based, with a focused on developed economies. Typically, these companies are found in Europe and Asia, but other countries may be represented.
Emerging Markets: These are companies in emerging markets - think developing nations, with many companies in South America and Africa.
Here are the four different types of stocks included in the report, along with a brief description and their Vanguard index fund:
International Developed Stocks (VTMGX)
Index fund provides low-cost, diversified exposure to large-, mid-, and small-capitalization companies in developed markets outside the U.S.
Real Estate (REITs)
Real estate is another asset class that has decent average annual returns. While there is some correlation between returns in the stock market and real estate returns, if you look at the underlying data, there are years when stocks are down and real estate is up (and vice versa).
While you might be able to start actively investing in real estate with as little as $500, investing in a real estate investment trust (REIT) can be another way to invest in real estate.
It can be difficult to compare individual real estate returns to the stock market, but you can look at the overall real estate market through a REIT. Here's a popular choice:
- Real Estate Index Fund (VGSLX) — This fund invests in real estate investment trusts—companies that purchase office buildings, hotels, and other real estate property.
Bonds
Bonds are historically a much safer investment, but with lower average annual returns. Bonds rarely have a negative return, but their maximum return is much lower than that of stocks. It can be a good idea to invest in bonds with some of your portfolio.
When you are younger, you can have a small amount of your overall portfolio in bonds, gradually increasing the percentage as you get closer to retirement.
- All U.S. Bonds (VBTLX) — This fund is designed to provide broad exposure to U.S. investment-grade bonds. Reflecting this goal, the fund invests in U.S. Treasuries and mortgage-backed securities of all maturities (short-, intermediate-, and long-term issues).
- International Bonds (VTABX) — This fund is designed to provide broad exposure to non-U.S. investment-grade bonds. The fund seeks to track the performance of an index that includes international government, agency, and corporate securities, mostly from developed countries, but also some emerging markets countries.
Start Investing Today
Here's our in-depth guide that shows you 10 solid ways to start investing with just $1,000.
Cash (T-Bills)
Cash and treasury bills (T-bills) are the most secure of just about any asset class. But while the value of your actual cash is unlikely to go down, the purchasing power of your cash often decreases each and every year. This is due to inflation, and is a good reason why you should not keep more than an emergency fund in cash.
- Cash (T-Bill) (VUSXX) — This fund at a minimum invests 80% of the assets in debt issued directly by the government in the form of Treasury bills. It may invest in other securities including, but not limited to debt issued by federal agencies that are sponsored, guaranteed, or owned by the federal government.
Wage Growth
When discussing investment returns by asset class, one of the biggest assets most people fail to think about is themselves. You are typically one of the strongest earning assets you have - especially early on in life. However, as you can see from the chart, the "return" on your wages is near the bottom of the asset return chart.
Wages have only averaged 3.51% in annual growth for the last 30 years. If you simply relied on just your income growth, you'll find yourself falling behind. It's essential that you take your extra money and invest it so that you can realize higher returns.
The Bottom Line
You have many choices for where to invest your hard-earned dollars, and each asset class comes with its own pros and cons. Generally speaking, the younger you are and the more years you have until retirement, the more risky that you can afford to be.
When you're in your 20s and 30s, you should have the majority of your portfolio in the asset classes with the highest average annual returns. You should also have a long-term investment horizon, and with the power of compound interest, you should be a millionaire in no time.
Pro-tip: A Robo-advisor is an investment management firm that automatically allocates your investments between stock and bond ETFs. Unlike a traditional financial advisor, computer software does much of the work. If you're overwhelmed by setting up your own asset allocation, a robo-advisor can do it for you. Check out a quick comparison below, or read the full list of the best robo-advisors.
Header |  | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Rating | |||
Annual Fee | 0.25% to 0.40% | 0.25% | 0.30% |
Min Investment | $0 | $500 | $50,000 |
Advice Options | Auto and Human | Auto | Auto and Human |
Banking? | |||
Cell |

Robert Farrington is America’s Millennial Money Expert® and America’s Student Loan Debt Expert™, and the founder of The College Investor, a personal finance site dedicated to helping millennials escape student loan debt to start investing and building wealth for the future. You can learn more about him on the About Page or on his personal site RobertFarrington.com.
He regularly writes about investing, student loan debt, and general personal finance topics geared toward anyone wanting to earn more, get out of debt, and start building wealth for the future.
He has been quoted in major publications, including the New York Times, Wall Street Journal, Washington Post, ABC, NBC, Today, and more. He is also a regular contributor to Forbes.
Editor: Claire Tak